Current location: Home > PRODUCTS > Next Generation Sequencing Series Products
PRODUCTS
(For Research Use Only)
Ovarian cancer is a malignant tumor that poses a serious threat to women's health. It ranks third in the incidence of malignant tumors in the female reproductive system, following cervical cancer and endometrial cancer, but has the highest mortality rate among female reproductive system malignancies. Ovarian cancer is often referred to as the "silent killer" because when symptoms appear and patients seek medical attention, about 70% of cases are already in advanced stages, resulting in low 5-year survival rates.
The most common type of ovarian cancer is epithelial ovarian cancer, accounting for approximately 80% of cases. Epithelial ovarian cancer can be further categorized into serous carcinoma (70-80%), endometrioid carcinoma (10%), clear cell carcinoma (10%), mucinous carcinoma (3%), and other rare types (<5%) based on pathological characteristics. Research has shown that different types of ovarian cancer carry different mutated genes, which can assist in histopathological classification and be used clinically for ovarian cancer risk assessment, optimizing treatment plans, and supporting genetic screening.
Furthermore, there is clinical evidence suggesting that molecular subtyping of ovarian cancer can be linked to individualized treatment, leading to improved patient survival rates. It has become an effective approach to guide ovarian cancer treatment.
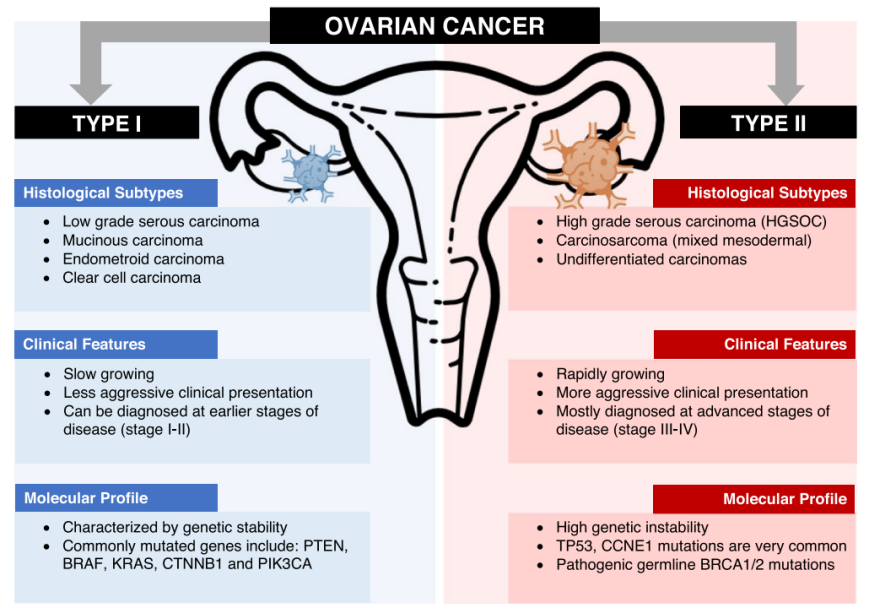
Molecular Cancer, 2022, 21(1): 114.
CSCO Guidelines - Molecular Characteristics of Different Subtypes
| Type | Common Immunohistochemical Expression | Common Gene Alterations |
High-grade serous carcinoma | p53 mutant expression (including nonsense mutations) WT1+ Pax8+ High Ki67 expression | TP53 mutation BRCA1/2 mutation |
| Low-grade serous carcinoma | WT1+,Pax8+,Wild-type p53 expression, Low Ki67 expression | BRAF mutation KRAS mutation |
| Endometrioid carcinoma | Estrogen receptor ( ER )+, Pax8+, Vimentin+, WT1-, Wild-type p53 expression | PTEN mutation CTNNB-1( beta-catenin) mutation ARID1A mutation |
| Clear cell carcinoma | HNF beta+, WT1-, ER- | ARID1A mutation PTEN mutation PIK3CA mutation |
Mucinous carcinoma | CK20+, CDX2+, CK7+, ER-, WT1- | KRAS mutation CDKN2A mutation TP53 mutation |
Malignant Brenner tumor | WT1-ER and PR negative or weakly + p16 focal+Wild-type p53 expression focal p16-positive, Wild-type p53 expression | PIK3CA mutation MDM2 amplification |
DETECTION CONTENT
| TP53 | BRCA1 | BRCA2 | KRAS | NRAS | BRAF |
| PIK3CA | CTNNB1 | PTEN | HER2 | EMSY | CCNE1 |
PRODUCT INFORMATION
| Product Name | Core Technology | Pack Size | Instruments Validated | Sample Type |
Human Ovarian Cancer Gene Mutations Detection Kit | RingCap® | 16 Tests/Kit 32 Tests/Kit | Illumina MGISEQ | Tumor tissue Peripheral blood |
DETECTION SIGNIFICANCE
1.Prognostic Assessment: Ovarian cancer is highly heterogeneous. Accurately classify the tumor tissues and suggest the prognosis of patients according to the molecular characteristics of different tissue subtypes, assisted by morphology and immunohistochemistry.
2. Treatment Guidance: Guide the use of PARP inhibitors to BRCA1 / 2 gene mutation; Guide the use of RAF / MEK inhibitors to BRAF gene mutationin patients with low-grade serous carcinoma; Suggest the use of cross-cancer or clinical trial drugs to other gene mutations.
3. Genetic Risk: Provide a basis for the diagnosis and subsequent diagnosis and treatment of hereditary tumors by detecting whether the proband or high-risk group carries germline mutations such as BRCA1 / 2.
FEATURES & ADVANTAGES
Ease of Use: Based on the independent patent technology RingCap®, Library preparation in 2 steps.
High Sensitivity: Detect gene mutations with an abundance as low as 5% in a 10 ng DNA sample.
Genetic Assessment: Conducting comprehensive exome sequencing and germline sequencing of the BRCA1/2 genes can assess familial genetic risk.
Molecular Subtyping: It aids in personalized precision treatment and improving the prognosis of ovarian cancer patients.
DETECTION PROCESS
1. Nucleic Acid Extraction
2. Library Preparation (3.5 hours total time)
3. Sequencing
4. Auto-data Analysis
5. Report