Current location: Home > PRODUCTS > Next Generation Sequencing Series Products
PRODUCTS
(CE-IVD)
BACKGROUND
The last three decades have witnessed steady, worldwide increases in the incidence of TC . Rates vary widely from country to country, with the highest figures (per 100 000 person-years) reported in Lithuania (15.5), Italy (13.5), Austria (12.4), Croatia (11.4) and Luxembourg (11.1). Estimated TC-related mortality rates, by contrast, are low (0.7 and 0.5 cases per 100 000 person-years for women and men, respectively) with considerably less regional and temporal variation[2].Thyroid carcinoma occurs two to three times more often in women than in men. Thyroid carcinoma is currently the seventh most common malignancy diagnosed in women.
FNA SAMPLE ASSISTED DIAGNOSIS
Definite diagnosis is the premise of tumor treatment. Ultrasound and ultrasound-guided US-FNA are the first choice for the screening of benign and malignant thyroid nodules. However, FNA cytology can also produce about 20%-30% uncertain results[1]. The 2023 BETHESDA SYSTEM FOR REPORTING THYROID CYTOPATHOLOGY(TBSRTC) recommend gene testing for Bethesda type III 、 IV or V nodules with uncertain US-FNA cytological diagnosis, which can assist in the diagnosis of benign and malignant nodules , the classification of thyroid cancer subtypes, and guide the follow-up treatment [2].
TBSRTC classification of malignant risk and management recommendations
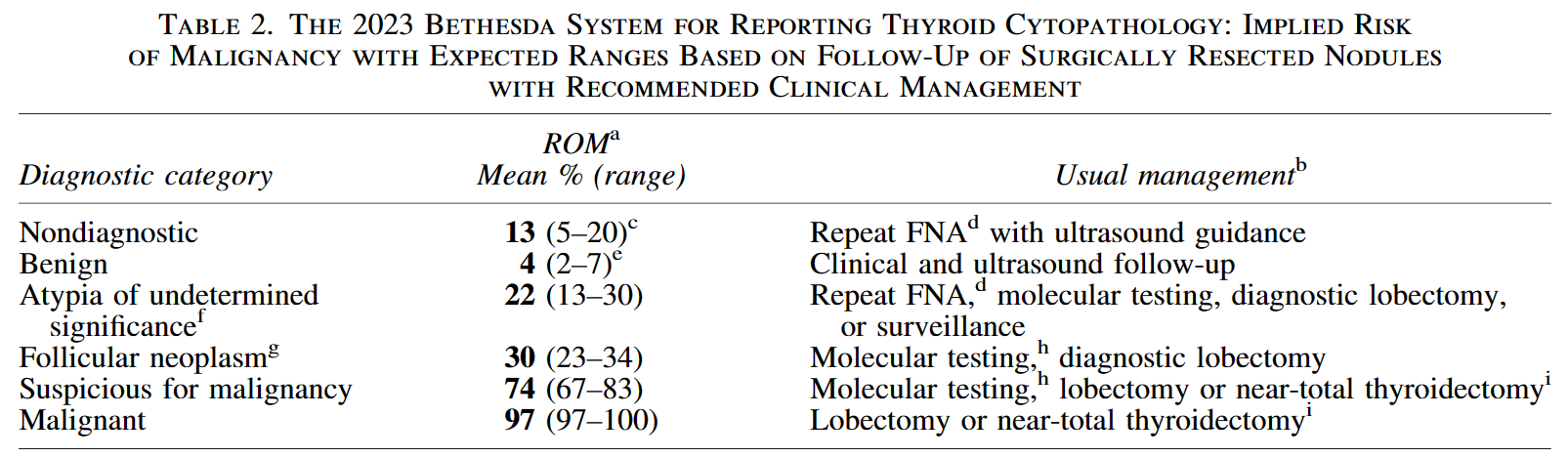
The 2023 BETHESDA SYSTEM FOR REPORTING THYROID CYTOPATHOLOGY
OTHER DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT TIPS
In addition, thyroid cancer gene detection can provide prompt information for the formulation of surgical plan, the use of targeted drugs, the diagnosis and treatment of hereditary thyroid cancer. Both FDA and NMPA have approved a variety of targeted drugs for the treatment of unresectable, recurrent and refractory differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC), medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) and undifferentiated thyroid cancer. Companion diagnosis of drugs includes RET fusion and mutation detection, BRAF V600E detection and NTRK fusion detection.
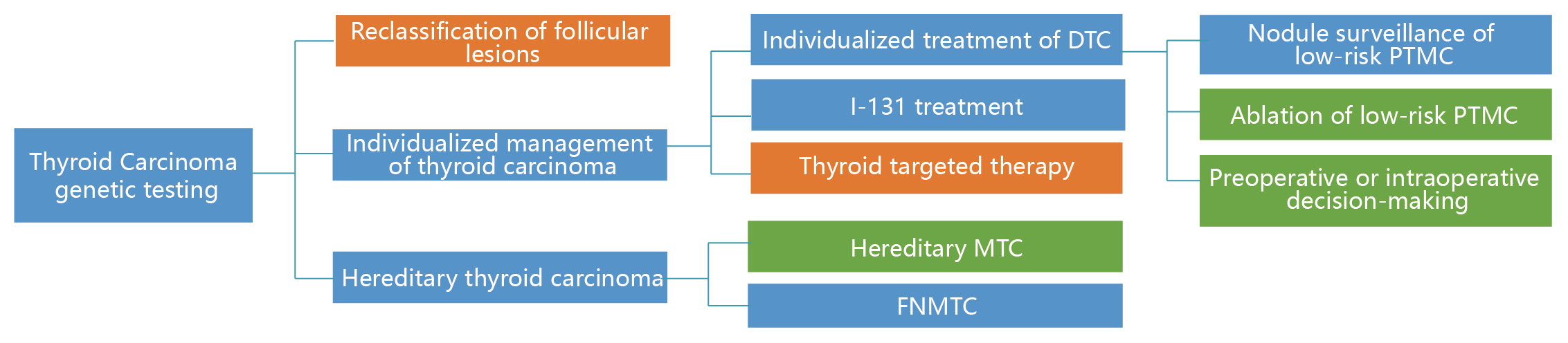
Note: papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (PTMC), familial non medullary thyroid carcinoma (FNMTC)
DETECTED GENES
The test kit is based on high-throughput sequencing, covering all common genes related to thyroid tumor typing, prognosis, medication and genetics recommended in NCCN guidelines, CSCO guidelines and expert consensus.
Mutation Type | Detection Gene | |||||
Mutation | BRAF | RET | KRAS | NRAS | HRAS | TERT-P |
TP53 | PIK3CA | AKT1 | CTNNB1 | EIF1AX | TSHR | |
GNAS | ZNF148 | SPOP | PTEN | |||
Fusion | 209 fusion forms of 87 genes including RET, NTRK1/2/3, PAX8, PPARγ, ALK, BRAF, RAF1, MET, THADA, etc. | |||||
PRODUCT INFORMATION
| Product Name | Core Technology | Pack Size | Instruments Validated | Sample Type |
Thyrcan TM Thyroid Cancer Gene Mutation Detection Kit | RingCap® | 16 Tests/Kit 32 Tests/Kit | Ion torrent Illumina MGISEQ | Tumor tissue,FNA (For germline detection, peripheral blood is required) |
DETECTION SIGNIFICANCE
1. Molecular diagnostics may be useful to allow reclassification of follicular lesions as either more or less likely to be benign or malignant based on the genetic profile.
2. DTC patients who are going to undergo surgery, radioactive iodine therapy or ablation therapy should be tested to determine the risk of tumor recurrence and formulate individualized treatment plans.
3. For patients with advanced thyroid carcinoma who are selected for targeted therapy, target genes should be detected to guide the selection of targeted drugs.
4. Patients with hereditary MTC and their family members should be tested to provide guidance information for diagnosis, treatment and prevention.
FEATURES & ADVANTAGES
1. Ease of Use: Based on the independent patent technology RingCap®, Library preparation in 2 steps.
2. Fast Results: The library preparation takes only 3.5 hours.
3. Comprehensive Coverage: Detects mutations in 16 genes and up to 209 fusion forms in 87 genes for individualized management of thyroid carcinoma .
4. High Sensitivity: It can detect gene mutations as low as 1% in 5ng FNA samples or 25ng tissue samples, and gene fusions as low as 200 copies/ul in RNA samples.
DETECTION PROCESS
1. Nucleic Acid Extraction
2.Library Preparation (3.5 hours total time)
3.Sequencing
4.Auto-data Analysis
5.Report
[1] NCCN Thyroid Carcinoma 2023 V3
[2] Thyroid. 2023 Sep;33(9):1039-1044.