Current location: Home > NEWS > Industry news
NEWS
PRODUCTS
Could you use targeted drug for he Low mutation abundance?
News source: Release time:[2022-12-09]
The abundance is the relative share of the weight of a chemical element in a natural body to the total weight of that body. When we receive a genetic test report, we can often see this reference value, which makes many patients wonder what is "abundance"?
The EGFR mutation, the most common mutation in lung cancer, as an example, "mutation abundance" can be briefly understood as the concentration of EGFR mutation frequency in total DNA, and some scholars define abundance as the ratio of EGFR mutation to wild-type copies.However ,there is no clear definition as so far.
Could mutation abundance predict the effect of targeted therapy?
Mutation Abundance and Efficacy of Generation EGFR-TKIs
In 2011, Prof. Yilong Wu's team designed a study to explore EGFR mutation abundance and the effect of targeted drugs using the characteristic that different assays have different sensitivities to detect EGFR mutations.
This study utilized two assays with different sensitivities, direct sequencing (10%) and ARMS (1%), to detect EGFR mutations in 100 patients with non-small cell lung cancer. And the patients were divided into 3 groups
Group H(High mutation abundance group):Mutation Positive by both DNA sequencing and ARMS
Group L(Low mutation abundance group):Negative by both DNA sequencing 、Positive by ARMS
Group W(Wild type group):Negative by both DNA sequencing and ARMS
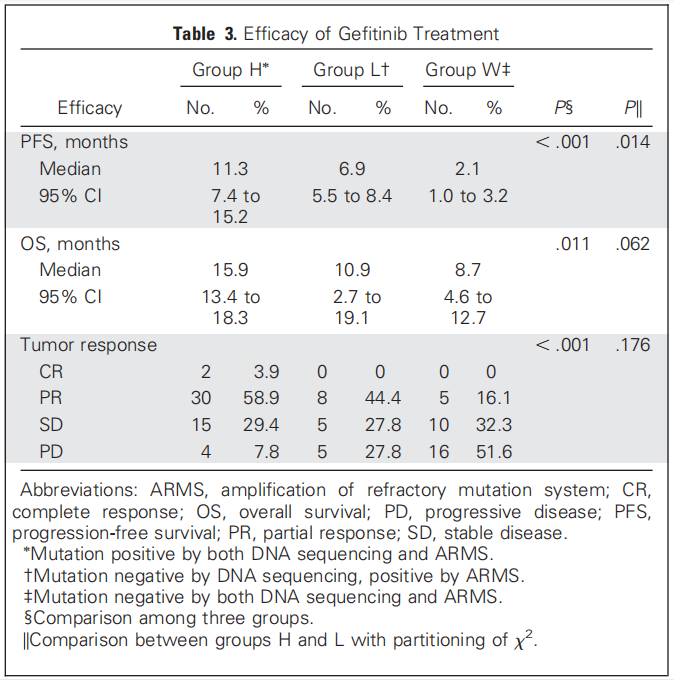
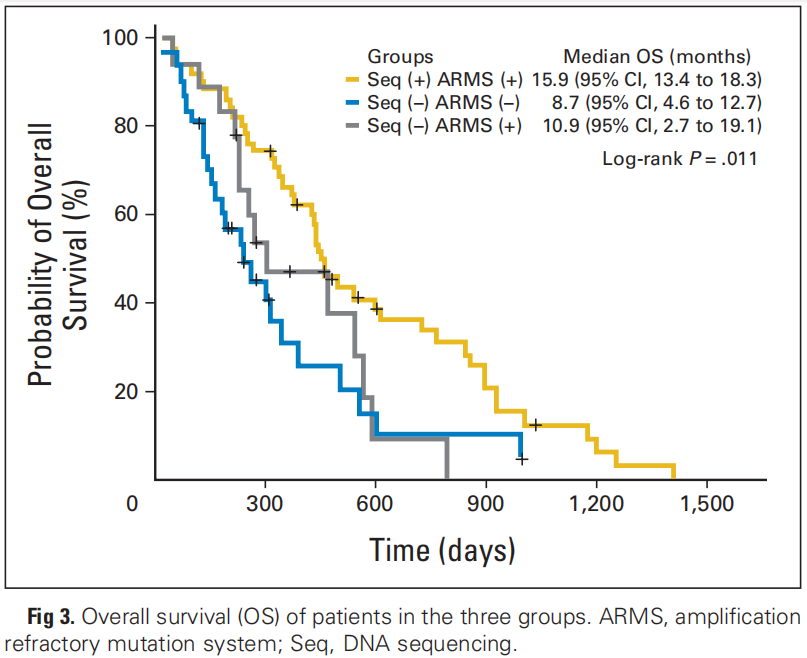
Study results.:
Group H,PFS 11.3,OS 15.9 month;
Group L, PFS 6.9个月,OS 10.9 month;
Statistically significant differences were found in both groups.
However, due to the limitations of the assay, the study did not quantify the abundance of EGFR mutations, but only grouped patients with two assays with different sensitivities.
In order to investigate the relationship between mutation abundance and the efficacy of targeted drugs in more detail, Prof. Cai-Cun Zhou's team initiated a study that enrolled 201 non-small cell lung cancer patients in clinical trials from 2008 to 2012 to determine the threshold of EGFR mutation abundance by ROC analysis.
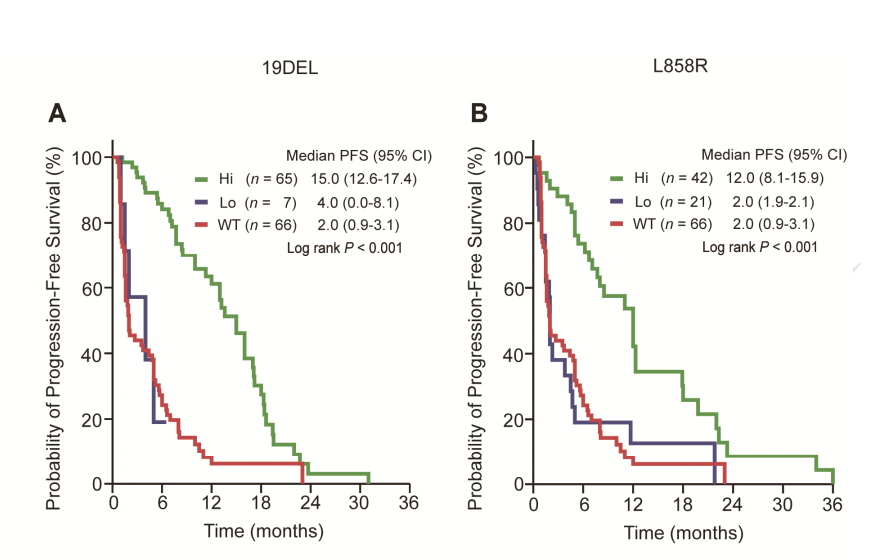
Study results.:
19del:Group H PFS is 15 month,Group L PFS is 4 month;
L858R:Group H PFS is 12 month,Group L PFS PFS is 2 month.
In the above figure green is the group with high EGFR mutation abundance, purple is the group with low EGFR mutation abundance, and red represents wild type. Whether it is 19Del or L858R mutation, higher abundance predicts better efficacy.
In addition. The NGS method was used in the study of Prof. Cai-Cun Zhou's team, and we can uncover some more interesting information through the following figure.
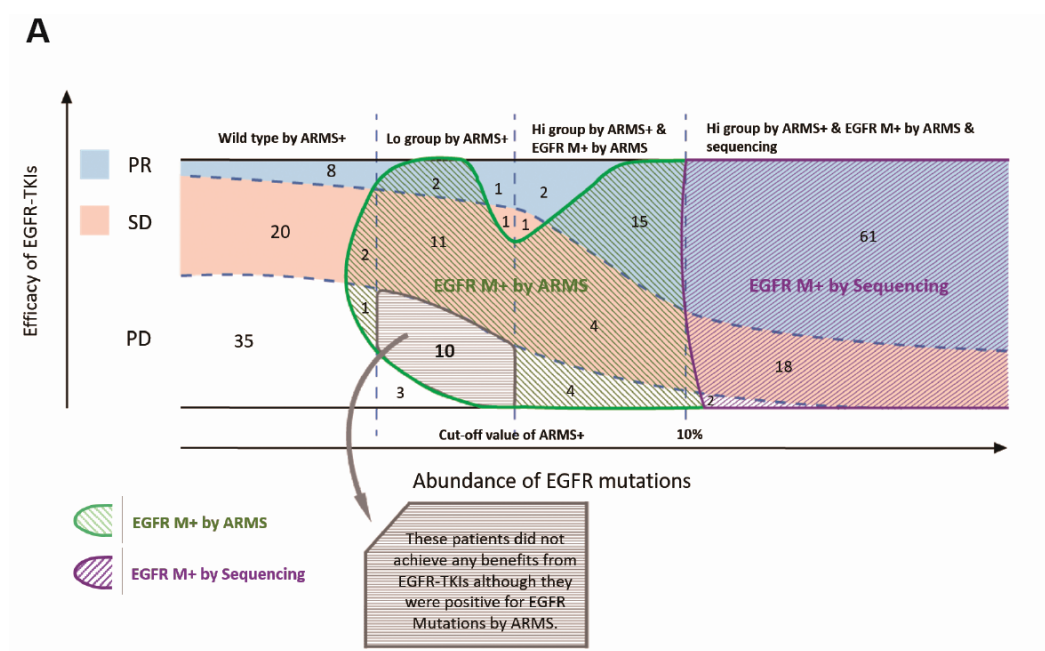
ü Patients with negative ARMS test, 8 patients in this group had PR with targeted therapy (12.6%). It is suggested that even if the blood is negative for EGFR by ARMS test, it does not necessarily mean that the targeted drug is ineffective. A retest with a more sensitive method could be considered to confirm the EGFR mutation status in this group of patients.
ü The number of PRs with targeted therapy increased gradually with the increase of EGFR mutation abundance, especially in the NGS-positive group, where a total of 61 patients (75.3%) achieved PR.It revealed a correlation between mutation abundance and the effect of targeted therapy.
Mutation abundance and the third generations of EGFR-TKIs
When patients are tested for T790M mutations after resistance to first- or second-generation targeted drugs, why do some patients do well on third-generation targeted drugs and others quickly become resistant to them?
A study published in 2018 may give an answer. The study enrolled 34 patients with non-small cell lung cancer who had a sensitive mutation in the EGFR gene: 19del, L858R, or other mutation: L861Q. To better understand this study, here we need to introduce 2 concepts.
ü act-EGFR: refers to 19del, L858R or L861Q mutations
ü T790M/act-EGFR: ratio of T790M mutation to act-EGFR mutation
This study analyzed the mutation frequency of act-EGFR and the ratio of T790M/act-EGFR in relation to the third generations of EGFR-TKIs, and two critical values of 2.6% and 0.22 were identified by ROC analysis, which are two more critical thresholds.
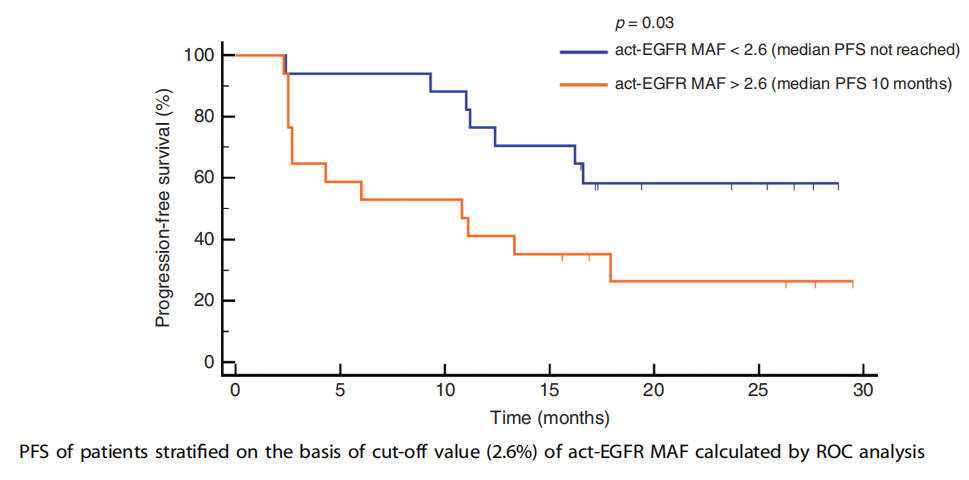
As shown above: When the mutation abundance of act-EGFR gene containing sensitive mutations such as 19del and L858R is less than 2.6%, patients have longer progression-free survival and better efficacy with third-generation EGFR-TKIs.
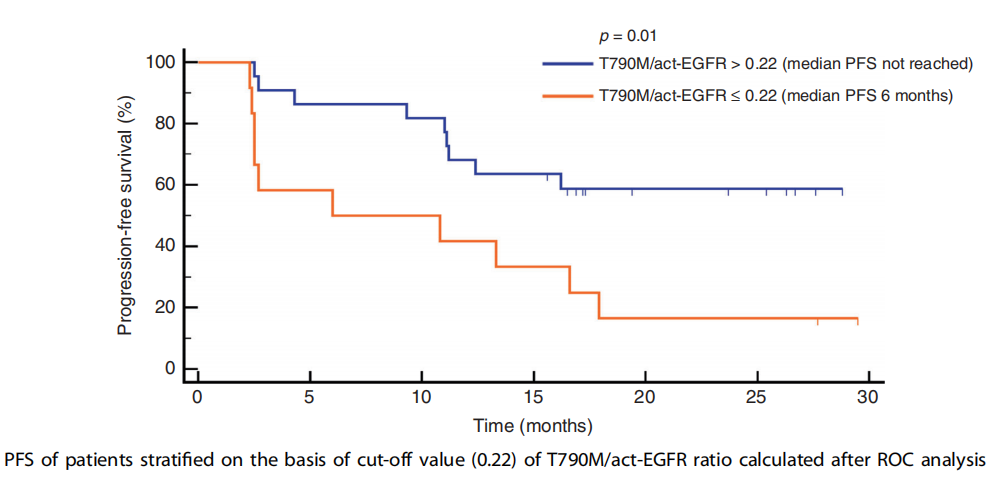
Meanwhile, when T790M/act-EGFR > 0.22, i.e., the ratio of T790M mutation to act-EGFR mutation > 0.22, patients have longer progression-free survival and better efficacy with third-generation EGFR-TKIs.
Oncology Multi-Gene Mutations Detection Kit developed by SpaceGen has been approved by CE and NMPA

With rapid detection, high sensitivity and multiple sample applicability for meet the different needs of clinical use.
Note: The data cited in this article suggest that EGFR mutation abundance is closely associated with the efficacy of EGFR-TKIs, but only for non-small cell lung cancer patients with EGFR mutations treated with EGFR-TKIs, and for patients with other cancers, please do not take the same position. Meanwhile, mutation abundance is affected by many factors such as tumor heterogeneity, patient's tumor load status, and testing platform, so please view the opinions and conclusions of this article rationally in the context of the actual situation.
References
[1]Zhou Q, Zhang X C, Chen Z H, et al. Relative abundance of EGFR mutations predicts benefit from gefitinib treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer.[J]. Journal of Clinical Oncology Official Journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, 2011, 29(24):3316-21.
[2]Li X, Cai W, Yang G, et al. Comprehensive analysis of EGFR-mutant abundance and its effect on efficacy of EGFR-TKIs in advanced NSCLC with EGFR mutations.[J]. Journal of Thoracic Oncology Official Publication of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, 2017, 12(9):1388.
[3]Marzia Del Re, et al., The amount of activating EGFR mutations in circulating cell- free DNA is a marker to monitor osimertinib response, British Journal of Cancer, 06 November 2018