Current location: Home > NEWS > Industry news
NEWS
PRODUCTS
Germline or Somatic mutations consensu in the real world, the role of BRCA1/2 in epithelial ovarian cancer
News source: Release time:[2024-06-07]
Background
Ovarian cancer is the most fatal gynecological cancer, which kills more than 200,000 people worldwide each year. The high mortality rate of ovarian cancer is largely due to the fact that at the time of diagnosis, ovarian cancer cells have already metastasized to the peritoneum, which means that there is little possibility of curing it. In fact, the overall 5-year survival rate for advanced epithelial ovarian cancer is very low, about 30% to 50%. With the understanding of the biology of epithelial ovarian cancer has been significantly improved, it also provides us with new targeted therapy and follow-up treatment [1].
BRCA1/2 gene mutation
BRCA1/2 is an important tumor suppressor gene, which is crucial to maintain the normal growth and proliferation of cells, and also the most important gene to maintain the function of cell HRR[2] . Various tumors harboring BRCA1/2 mutations are sensitive to PARP inhibitors. In the SOLO-1 study, patients with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer harboring germline or somatic BRCA1/2 mutations were treated with olapari maintenance therapy after initial therapeutic response. Compared with placebo, the risk of recurrence or death of patients decreased by 70%, and the median PFS was extended by more than 3 years [3]. BRCA1/2 germline mutation is also associated with genetic susceptibility to tumors [3].
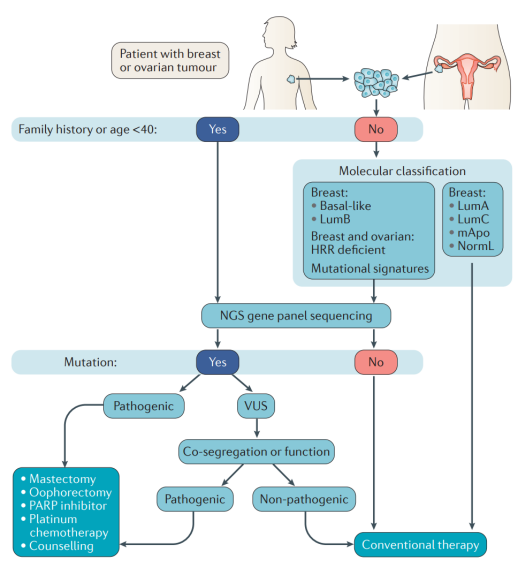
Bring about breast and ovarian tumor clinical management Suggestions
Literature Review-Relationship between Embryonic Lines and Systems in the Real World: The Role of BRCA1/2 in epithelial ovarian cancer [5].
Between 11 April 2021 and 11 October 2023, 442 tumor samples from 412 patients were tested with Myriad's myChoice®CDx. Tumor cell content ranged from 5% to 80% (tumor cell content was not provided for 61/442 [13.8%] samples). The failure rate of tumor BRCA1/2 detection was 10.2%(45/442 tumors). Tumor cell content ranged from 5% to 65% in samples that failed tumor detection (tumor cell content was not provided in 10 of 45 samples). Two or more tumor samples from 29 patients were tested with failure (tumor BRCA1/2 and GIS testing); 23/29 patients)or because the patient was erroneously detected twice (6/29 patients). Tumor BRCA1/2 testing was successful in 382 patients. Of these, 15 patients (3.9%) were not tested for germline BRCA1/2.
The study group included 367 patients who successfully underwent tumor and germline BRCA1/2 testing (Table 1). The majority of these patients were diagnosed as having advanced, high-grade, non-mucinous epithelial ovarian cancer.
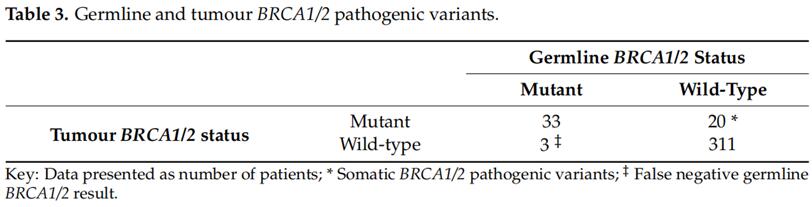
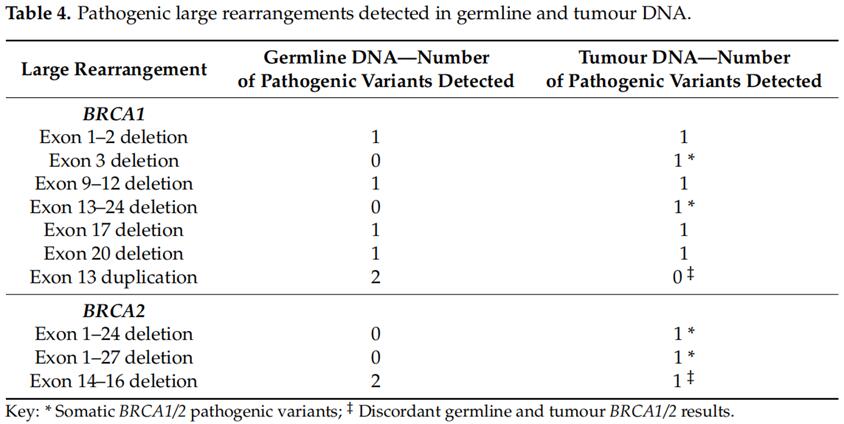
Germline BRCA1/2 testing was performed in all patients with pathogenic variants of BRCA1/2 detected in tumor DNA. Of the 36 germline BRCA1/2 pathogenic variants, 33 were detected in tumor DNA. The identity of the pathogenic variant of germline BRCA1/2 in germline and somatic tumor DNA was 91.7%(33/36) (Table 3). All small fragment sequencing BRCA1/2 pathogenic variants were detected in germline and somatic tumor DNA. The undetected germline BRCA1/2 mutations in the tumor DNA of the three germ line tumors were large fragment rearrangements including two BRCA1 exon 13 repetitions (n = 2) and one BRCA2 exon 1-24 deletion (n = 1, Table 4).
Conclusion and discussion
Conclusion: The concordance between germline and somatic BRCA 1/2 pathogenic variants in a real-world large cohort of patients diagnosed with epithelial ovarian cancer. If Myriad myChoice®CDx is used for tumor HRD, our data support a test model for germline and somatic tumor BRCA 1/2 detection in all diagnosed patients with epithelial ovarian cancer < 79 years of age, and only patients with pathogenic variation of tumor BRCA 1/2 ≥80 years of age need to undergo germline BRCA 1/2 detection.
Discussion: The main limitations of this study are moderate sample size and single-center state. Nearly 4%(15/382) of the study groups did not undergo germline BRCA 1/2 testing. A review of the clinical records of these patients shows that almost all patients who refused to undergo embryology testing or who had clinically poor prognostic factors died before undergoing embryology testing. Besides, a small number (12/367) of subjects in the study group were not diagnosed with high-grade ovarian cancer and therefore were not eligible for tumor HRD testing.
It should also be noted that no neoplastic BRCA1/2 assay has been shown to differentiate between germline and somatic pathogenic variants, and therefore germline assays should be performed in all patients with neoplastic BRCA1/2 pathogenic variants.
Human BRCA1/2 gene mutation detection kit
"Human BRCA1/2 gene mutation detection kit" introduced by SpaceGen enables clinicians to comprehensively assess the gene status of patients, optimize patient management and formulate personalized treatment plans for patients.
Test item
Project name | core technology | Project specifications | Adapter platform | Sample type |
Baikexin Human BRCA1/2 gene mutation detection kit | RingCap® | 16 test/box 32 test/box | Ion Torrent、 Illumina、 MGISEQ | Tumor tissue sample |
Peripheral blood/oral swab/saliva |
Detection significance
1. Providing a basis for the diagnosis and subsequent diagnosis and treatment of hereditary tumors by detecting whether a proband or a high-risk group carries BRCA1/2 gene germline mutation;
2. To evaluate the sensitivity of patients with BRCA1/2 mutation malignant tumor to PARP inhibitors such as olapari.
Detection Advantage
1. Simple operation: the patented RingCap® technology was independently developed, and the library construction only required two steps and could be completed in 3.5 hours.
2. High sensitivity: gene mutation with content as low as 5% in 10 ng DNA sample can be detected.
3. Comprehensive detection: Since there is no high-frequency mutation hot spot in the BRCA1/2 gene, sequencing the coding region and the adjacent boundary region can ensure the comprehensive detection.
4. Strictly professional: comprehensive and strict quality control standards, automatic analysis and double review by professional team, so as to truly achieve a comprehensive and accurate interpretation.
References
[1] Guidelines for BRCA1/2 gene detection based on next-generation sequencing technology (2019 )
[2] China Expert Consensus on Detection of PARP Inhibitor-related Biomarkers in Ovarian Cancer
[3]N Engl J Med, 379, 26(2018): 2495-250
[4]Nat Rev Cancer. 2016 Sep; 16(9): 599-612.
[5]Cancers 2024, 16, 177. https:// doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010177
Statement: This article is only for sharing, if it involves copyright issues, please contact us as soon as possible, we will correct the first time, thank you!