Current location: Home > PRODUCTS > Real Time PCR Series Products
PRODUCTS
Gocsen®
(CE-IVD)
Cervical cancer is a malignant tumor that seriously threatens women's health. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in reducing cervical cancer mortality rates. Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN, original CIN1) can be classified into low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL, original CIN2 and CIN3) and high-grade lesions (HSIL). Timely detection and treatment of HSIL, which has the potential to progress to invasive cervical cancer, are the main objectives in the management of cervical cancer, aiming to minimize the risk of invasive cervical cancer development.
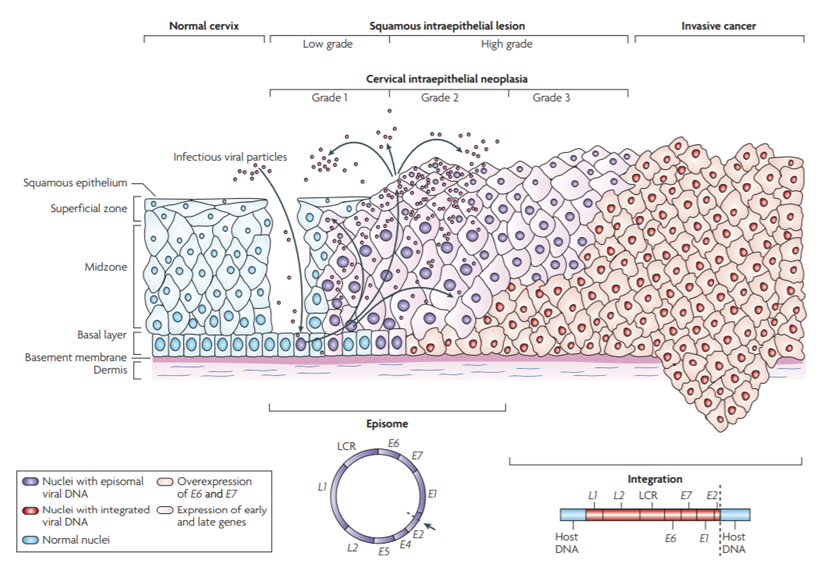
HPV Infection and Cervical Lesion Progression[1]
Research has revealed that genetic abnormal changes are a crucial mechanism in tumor development, and DNA methylation can induce tumor occurrence by silencing key tumor suppressor genes. PAX1 protein plays a significant role in embryonic development by regulating cell proliferation and inducing directed cell migration, contributing to the formation of essential organs. There is a close relationship between the highly methylated PAX1 gene promoter region and cervical cancer. Quantitative detection of PAX1 gene promoter methylation levels in cervical exfoliated cells can be utilized for cervical cancer screening and the management of precancerous lesions.
The greatest advantage of PAX1 gene methylation testing lies in its high specificity, with its methylation level highly correlated with cytological grading and the severity of cervical lesions [2]. It can serve as a triage test after HPV testing is positive or when the TCT results show atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US) before colposcopy. By implementing PAX1 methylation testing, the number of unnecessary colposcopies and biopsies in patients can be reduced by 30% to 60% [3-4].
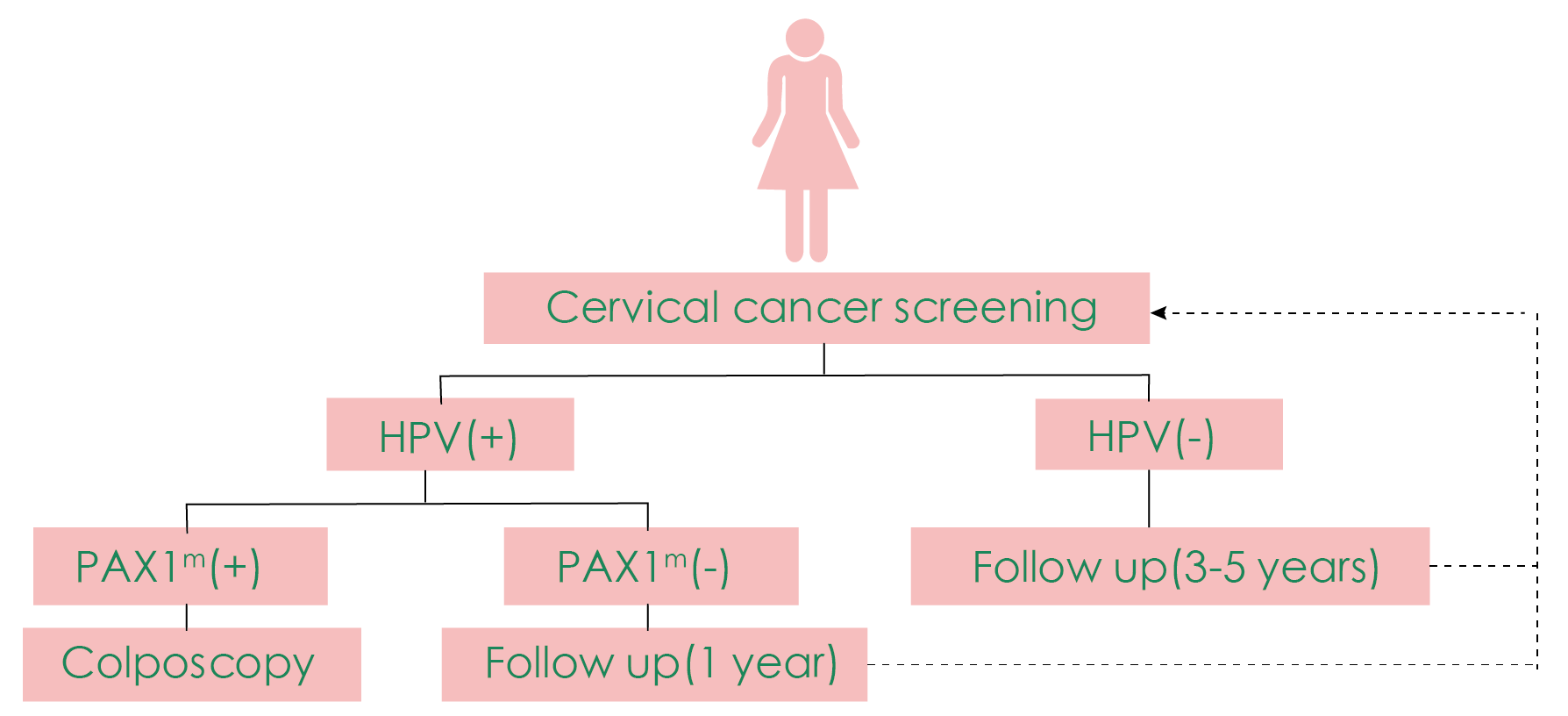
The use of PAX1 methylation for triage before colposcopy [5].
In addition to triage, PAX1 methylation can be used in combination with HPV for cervical cancer primary screening, resulting in a substantial increase in sensitivity without sacrificing specificity [6]. PAX1 methylation also shows significant performance in detecting cervical adenocarcinoma [7]. Moreover, some studies suggest its potential application value in disease monitoring after treatment for cervical lesions or cervical cancer.
INTERPRETATION OF RESULTS
Project Name | Interpretation of Results | Clinical Significance |
PAX1 Gene Methylation Detection Kit | Strongly Positive | Indicates cervical lesions, suggests further examination or taking tissue specimens for pathological diagnosis to determine the treatment plan. |
Weak Positive | Follow-up is closely conducted and regular methylation testing is recommended. | |
Negative | Perform routine testing. |
RODUCT INFORMATION
Product Name | Core Technology | Pack Size | Instruments Validated | Sample Type |
GocsenTM PAX1 Gene Methylation Detection Kit | PAP-ARMS® | 20 Tests/Kit | ABI7500, ABI7300, ABI StepOne Plus, LightCycler480, Bio-Rad CFX96, etc. | Cervical exfoliated cells |
APPLICABLE PEOPLE
1. High-risk HPV-positive, or non-16/18 high-risk HPV-positive patients;
2. Patients with TCT result of ASC-US and above;
3. Population of universal screening for cervical cancer;
4. People with recurrent inflammation of the cervix, recurrent infection or unexplained vaginal bleeding;
5. Patients with cervical lesions or cervical cancer monitoring after treatment.
FEATURES & ADVANTAGES
1. High specificity: Compared with other mainstream screening methods, PAX1 methylation detection has high specificity and can be used to triage HPV-positive patients;
2. Accuracy and Reliability: Use sub-packed PCR tube to effectively avoid cross-contamination.
3. Ease of Use: Based on technology PAP-ARMS®, one step detection in 90 mins.
4. Great versatility: Validated on the most common qPCR machines with stable results.
5. Strict Quality Control: Internal and external controls and negative and positive controls were included in the assay to ensure the credibility of the results.
DETECTION PROCESS
1.Nucleic Acid Extraction
2.Modification
3.Set up qPCR
4.Amplification
5.Data Analysis
REFERENCES
[1] Nat Rev Cancer. 2007 Jan;7(1):11-22.
[2] Cancer Manag Res. 2020; 12: 2567–2576.
[3] Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2014 Jun;24(5):928-34.
[4] Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 22; 8 (37): 62274-62285.
[5] Mol Genet Med. 2019 Mar;7(3):e506.
[6] Int J Cancer. 2008 Jul 1;123(1):161-7.
[7] Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2014 Feb; 24 (2): 201-9.